● Around two-thirds of local organisations acknowledge gap in understanding how digital
technology can facilitate achieving sustainability goals
● 81% businesses in Malaysia concerns high energy consumption of digital technology
● 75% of local businesses cite security risks as a major concern that could hinder broader adoption
of advanced digital technologies.
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 11 March 2025 – Over three quarters of businesses 76% across Asia,
Europe and the Middle East are intrigued by the potential of digital technologies, including AI
and cloud computing in driving sustainable development, according to the latest survey report
titled “Tech-Driven Sustainability Trends and Index 2024”, commissioned by Alibaba Cloud, the
digital technology and intelligence backbone of Alibaba Group. However, the substantial energy
consumption associated with these technologies is still reflecting a key barrier to broader
adoption, as 61% of respondents still express concerns over the matter.
The survey highlights Malaysia’s evolving stance on AI adoption and sustainability, revealing
both enthusiasm and caution among businesses. Specifically, 76% of Malaysian businesses are
actively adopting digital technologies to accelerate sustainability progress, with 77% intrigued
by AI’s potential to drive sustainability innovation. Despite this optimism, 62% of Malaysian
businesses acknowledge the gap in understanding how digital technology can assist in achieving
sustainability goals and 81% of businesses believe that the substantial energy consumption of
digital technologies such as powering AI may outweigh its benefits. Additionally, 75% cite
security risks as a major barrier to adopting advanced digital solutions more broadly.
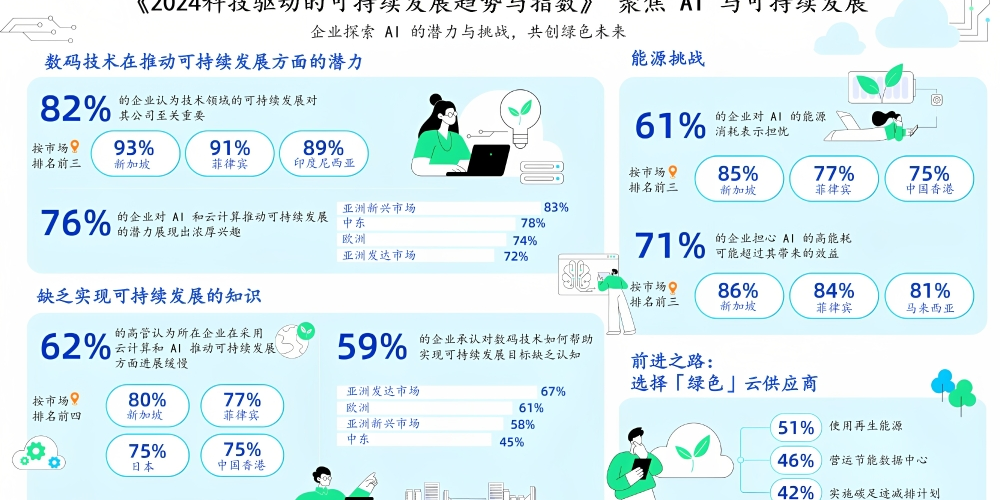
Regional Variations in AI Adoption and Sustainability Efforts
Despite this optimism, 59% businesses acknowledge the gap in understanding how digital
technology can assist in achieving sustainability goals with Asia leading at 63%, followed by
Europe at 61% and the Middle East at 45%. Around two thirds 62% of executives believe their
organisations are lagging in adopting cloud computing and AI to accelerate progress towards
sustainability goals. This concern is particularly noted in Singapore 80%, the Philippines 77%,
Japan 75% and Hong Kong SAR 75%, indicating a pressing need for organisations to accelerate
their technological adoption to advance sustainability.
Overall, 82% of businesses agree that sustainable development in technology is paramount for
their companies, with markets like Singapore 93%, the Philippines 91%, and Indonesia 89%
leading the charge. Companies increasingly recognise the multifaceted benefits of adopting
digital technologies for sustainability including cost savings, improved operational efficiencies,
and enhanced compliance with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) regulations.
AI and machine learning are viewed as the most crucial digital technologies for advancing
corporate sustainability, with businesses in the Middle East 52% placing greater emphasis on
their importance compared to Europe 41%, emerging Asian markets 40% and developed Asian
markets 36%.
However, the survey reveals a notable concern: 61% of respondents fear that the high energy
consumption associated with digital technologies may hinder widespread AI adoption. This
concern is even higher in Singapore 85%, the Philippines 77% and Hong Kong SAR 75%.
Furthermore, 71% of businesses believe that the substantial energy consumption of digital
technologies such as powering AI may outweigh its benefits with the highest concerns from
Singapore 86%, the Philippines 84% and Malaysia 81%.
The report also highlights the importance of selecting technology providers that prioritise
sustainability. When selecting a “green” cloud provider, approximately half of the businesses
prioritise those that use renewable energy 51%, maintain energy-efficient data centers 46%,
and implement carbon footprint reduction initiatives 42%.
Malaysian Businesses Prioritise AI and Machine Learning for Sustainability but Face Adoption
Challenges
The survey reveals 88% of Malaysian businesses agree it is important to the company that
technology is developed sustainably. To add to the concerns highlighted earlier, 68% believe
companies are lagging in cloud computing and AI adoption to meet these goals. This hesitation
is driven by barriers such as knowledge gaps 38%, cost constraints 30%, and lack of technical
capabilities 31%.
89% of business leaders acknowledge technology’s pivotal role in achieving global sustainability
targets with Malaysian companies ranking AI/Machine Learning 46%, Collaboration and
Communication tools 34%, and IoT 33% as the top three digital technologies critical to
advancing corporate sustainability goals. When selecting technology providers, Malaysian
businesses prioritise cost-effectiveness 52%, strong customer support 48%, and data privacy
commitments 40% highlighting the key factors that influence their digital adoption strategies.
Alibaba Cloud’s Commitment to Green AI and Open-source Innovation
“With feedback from decision-makers across 13 markets, the survey report sheds light on the
current attitudes and challenges businesses face in adopting AI and cloud computing for
sustainability,” said Selina Yuan, President of International Business, Alibaba Cloud
Intelligence. “At Alibaba Cloud, we are committed to supporting businesses on their
sustainability journeys with scalable and sustainable solutions. By pledging to use 100% clean
energy by 2030 and improving the energy efficiency at our global data centers, as well as
optimising Generative AI capabilities such as large language models (LLMs) performance, AI can
be a powerful tool to improve efficiency and optimise energy consumption.”
Alibaba Cloud has made notable progress in its green cloud initiatives. In the fiscal year ending
March 31, 2024, the average power usage effectiveness (PUE) of the company’s self-built data
centers improved to 1.200 from 1.215 the year before, with 56% of the electricity consumed
coming from clean sources. Additionally, Alibaba’s green computing infrastructure has enabled
clients to reduce their emissions by 9.884 million tons, a remarkable increase of 44% year-on-
year.
In addition, Alibaba Cloud is at the forefront of democratising AI through its open-source
initiatives, making advanced AI technologies accessible and affordable for businesses of all
sizes. By releasing cutting-edge open-source models from its proprietary large language model
Qwen family, including Qwen2.5-VL and Qwen2.5-1M and its video foundation model Tongyi
Wanxiang (Wan), Alibaba Cloud empowers developers to create task-specific AI applications
that are both efficient and cost-effective. These open-source models have already inspired over
100,000 derivative models on Hugging Face, showcasing their global adoption and versatility. By
promoting smaller parameter models, Alibaba Cloud reduces the cost and energy consumption
of AI training and deployment, fostering a collaborative ecosystem that drives energy-efficient
innovation.
Conducted with 1,300 decision-makers across 13 markets, including Malaysia, “Tech-Driven
Sustainability Trends and Index 2024” aims to provide valuable insights into the evolving
landscape of corporate sustainability. The survey report underscores the essential role of
technology in driving impactful change, while highlighting the need for businesses to adopt AI
and cloud computing responsibly to address energy consumption concerns and bridge the gap
in sustainability efforts.
About the Survey
Alibaba Cloud’s “Tech-Driven Sustainability Trends and Index 2024” was independently
conducted by Yonder Consulting, a business consulting firm, with advisory, design and
analytical support from The Purpose Business, a sustainability consultancy. The survey collected
feedback from May 10 to June 19, 2024, involving 1,300 business leaders and senior
management from various industries, including technology and communications, finance,
infrastructure, renewable resources, healthcare, transportation, retail, and manufacturing.
Respondents were located across 13 markets in Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines,
Thailand, Hong Kong SAR, Japan, Singapore and South Korea), Europe (France, Germany, and
United Kingdom), and the Middle East (Saudi Arabia and the UAE). In this survey, developed
Asian markets refer to Hong Kong SAR, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea, while emerging
Asian markets include Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand.